Sometimes you have some data in a column, and you want to change it in some way. You might want to multiply it by a number, take a square root - whatever.
With the column transform feature, you can apply a function to all the data in the column at once, creating either:
- A new set of values in the same column
- A new column to the right of the original one
To do this, click the column transform button on the column header:
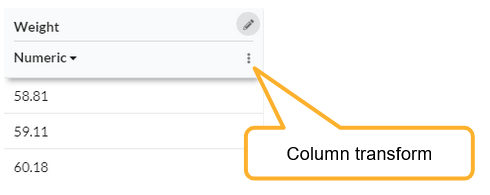
You can then choose between replacing the data in this column, or creating a new column.
You then get to specify the function, and the new column name (if relevant):
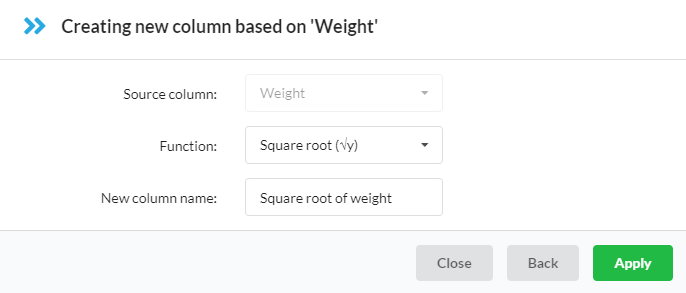
Available functions
Here is a list of the available transform functions.
- Y represents the value in the original column
- K is an optional value, required for some of the transforms. For example to convert 'Year' to 'Age' you might do Negate (k - y) and have a constant k = 2024.
- K can also be taken from another column, so you can e.g. multiply two columns together.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Add (y + k) | Add a number (k) to each value (y) |
| Subtract (y - k) | Subtract a number (k) from each value (y) |
| Multiply (y × k) | Multiply y by k |
| Divide (y ÷ k) | Divide y by k |
| Negate (k - y) | Subtract k from y (If k = 0, this is inverting the sign of y) |
| Invert (1 ÷ y) | Invert y |
| K divided by y (k ÷ y) | Divide y into k |
| Absolute value - abs(y) | Make y values always positive |
| Square (y2) | Square of y |
| Square root (√y ) | Square root of y |
| Power (yk ) | Raise y to the power of k |
| Log base 10 (log10 y ) | Base 10 logarithm of y |
| Log base e (log10 y ) | Base e logarithm of y (natural logarithm) |
| Exponent (ey ) | Raise e to the power y |
| Round (rnd) | Round to K digits after decimal point |
| Precision (prec) | Round to K significant digits of precision |
| Ranking - rank(y) | Rank values in column numerically and replace with a number representing their order in the ranking. Equal values get the same ranking. |
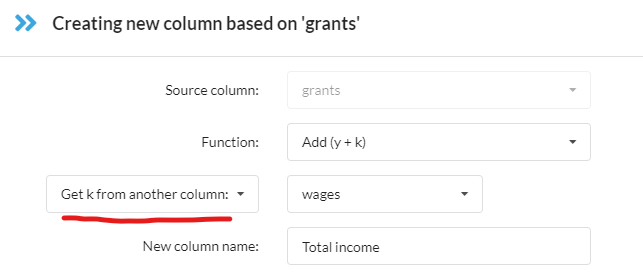
Functions of two columns
This is done by specifying K as coming from another column, as in this simple example:
Multiple transforms
You can create a sequence of transforms, if your data require this. For example, you could:
- First transform the number with a multiply or divide (convert inches into metres)
- Then take the square of that result (metres into square metres for area)
Errors
Some of these mathematical functions cannot handle all possible input values. For example:
- You can't take the square root of a negative number
- You can't take the logarithm of zero
- You can't divide anything by zero (OK you can, but you get "infinity" as the result!)
These errors will be flagged and you will get a warning if you are trying to apply an "impossible" transform.
Differentiation (slopes)
We don't currently have a function to differentiate column values (it's on the roadmap) but you can achieve the same (or similar) result by making a graph with a regression line, and then adding slope markers which give you the slope of the line at each point. You can then create a new column of data from these slope values. See this article on slopes and residuals for how to do this.