A categorical variable can affect another by overriding its otherwise-defined (default) distribution.
In this example, we have the variable Sex affecting the distribution of Handedness (as in left- or right-handed). More males are left-handed than females.
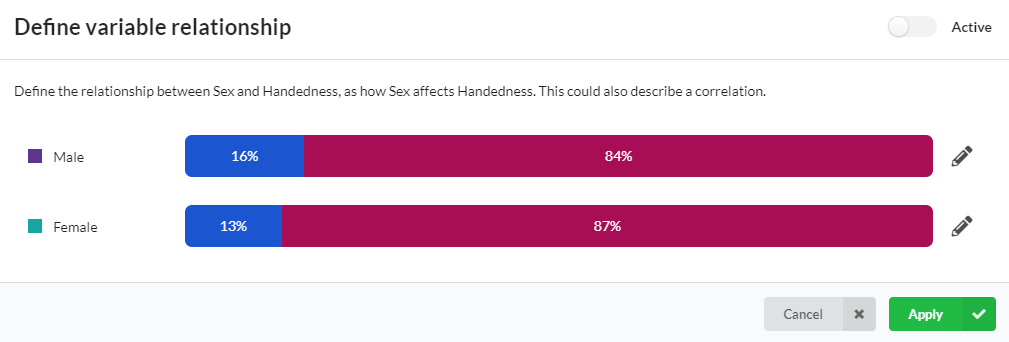
The simulation will operate by first generating the values of the first variable in the "chain of effects" - here it is Sex - and then generating the Handedness, depending on the value of Sex assigned to each sample.
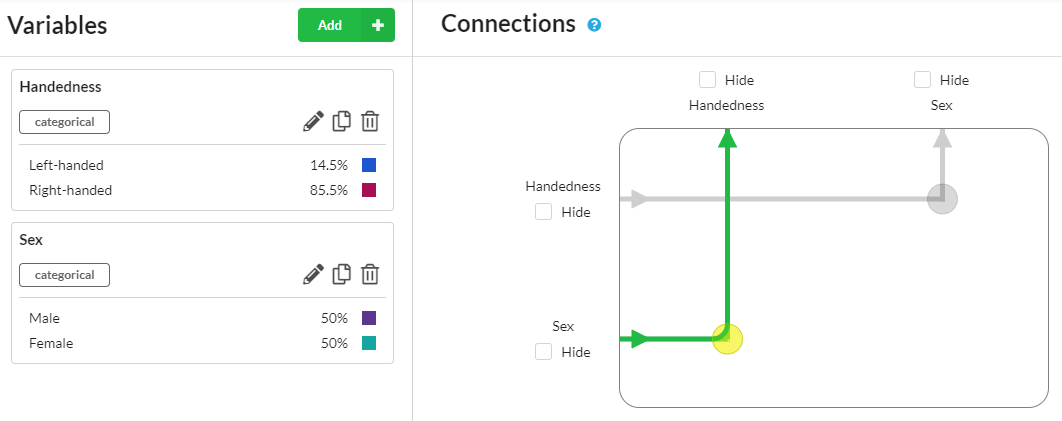
It's important to note that this relationship could have been defined in the reverse direction.